
FMCG represents the abbreviation for Fast Moving Consumer Goods, similar to consumer packaged goods that are relatively inexpensive and popular. The FMCG industry is characterized by high levels of turnover mainly because these products are popular with most people. It is an industry with high-volume sales, a relatively high turnover rate, and necessary products for daily consumption. The success of the FMCG and CPG industries lies in providing unique products, distribution channels, and locations to sell them.
What is Location Data for the FMCG Industry?
Location Intelligence for the FMCG industry involves using geographical data such as maps and real-time information to support the efficient positioning and marketing of products. FMCG business owners can use it to understand the foot traffic and distance of competitors and customers to their stores and business locations to ensure that they make necessary corrections to be closer to their customers and avoid competition with other established stores. For instance, when selecting a new store location, the FMCG can employ Location Intelligence information regarding traffic in surrounding areas, including restaurants, shopping centers, parks, etc. Hence, understanding the capabilities of customer flow and competitors’ presence can help determine the most lucrative areas.
Location data is especially important for such decision-making since it offers specific information about particular places, such as addresses, coordinates, and visitor characteristics. This assists FMCG companies in determining appropriate locations for opening new stores or the best routes for supplies.
Location Data in the FMCG industry is not just about determining where stores, products, or channels should be positioned. It comprises data from multiple purchases at retail shops and additional data obtained from consumers’ handheld devices such as GPS, W-Fi, or cell towers. This information is useful for understanding consumers’ movement and interactions in the physical environment, buying behaviors, and engagements with goods and information.
This data is essential to FMCG marketers. It enables them to tailor their promotional strategies to reflect actual customer behaviors in the market, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the promotional efforts. In this way, FMCG businesses can achieve more results by considering the viewers’ journeys through various contexts and using this knowledge to improve different aspects, starting from product placement and ending with advertising campaigns.
How Can Location Intelligence Help You Find the Best FMCG Distributors?
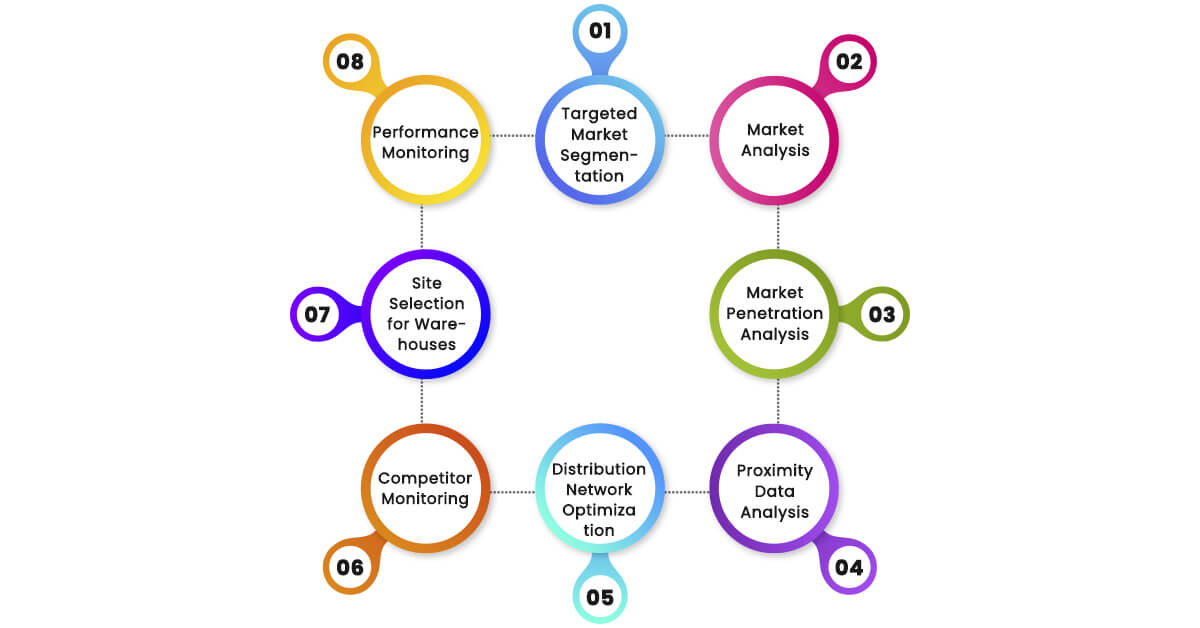
Location intelligence data assist in forming a connection between the virtual environment and the natural world to facilitate better decision-making about a diverse range of aspects, from target market campaigns to shipping network routes.
1. Targeted Market Segmentation
To expand your business, it is important to analyze your target segments and understand customers’ preferences in those segments. This means selecting the ideal cities, regions, or countries to invest in. Location intelligence allows you to discover where your target segment is and what they are spending. It assists you in identifying the right channel that will help distribute the products.
2. Market Analysis
When businesses want to establish their operations and sustain themselves in the market for a longer period of time, they must understand customer demand and where and when they shop. Location intelligence provides such data by looking at who lives in a specific area, how many people visit particular places, and details about the competitors. Understanding these trends assists a businessman in selecting a proper distributor through which they can easily reach to their target segment.
3. Market Penetration Analysis
Businesses with Location Intelligence will display where to penetrate a particular market with their products, such as supermarkets, retail shops, and convenience shops. This can be done by knowing the places people visit frequently to facilitate accessibility of the products. In this manner, distributors can continuously monitor these areas visited by the public to relocate your products to areas with a high likelihood of purchase.
4. Proximity Data Analysis
The location Intelligence allows businesses to identify distributors within proximity to the target market. The closer depots are to each other, the shorter the time taken and the less costs incurred in distributing products to the customers. Expanding smartly also helps in discovering new areas and potential markets, that is the areas where there is little supply of products already. This can be a great opportunity to grow if one remains employed in the organizations or new entities that will be created from the mergers.
5. Distribution Network Optimization
Location Intelligence is valuable and assists you in understanding issues with your current distribution, including poorly served regions or non-optimal routes. The information gathered from this will help to improve the efficiency of your distribution systems, cost, and providing products at the demanding market segment.
6. Competitor Monitoring
Location Intelligence helps businesses to understand competitors’ actions, market segments, and strategies. With this knowledge, they can identify areas where they can improve or areas the competition does not cover. If competitors are not there on a particular aspect, it is a positive sign to establish the market and expand the reach by providing goods and services. This helps businesses boost their revenue and take a competitive advantage.
7. Site Selection for Warehouses
The location of the distribution centers and the warehouses will require considerable consideration. Location Intelligence involves choosing the right location from all the options, including roads close to the places, proximity to customers, and population density. It also assists in determining the cost of land, availability of workers, and legal framework in the selected location to fulfill business goals regarding the specific area.
8. Performance Monitoring
Location Intelligence enables businesses to assess the effectiveness of the distribution channels through sales, customer satisfaction, and market share within a specific region and market segment. They can allocate additional resources to a location that appears to be performing well. If an area is having trouble, they can proactively determine the reason and address the issue.
Use of Location Data in FMCG Business

Location data is extremely relevant in the FMCG industry because it primarily determines operational efficiency and effectiveness. This analytical approach also helps the business compete successfully with other counterparts and make necessary adjustments to satisfy customers’ needs in the long run due to the volatility of market trends. Here’s why it’s so important:
Enhanced Decision-Making
Location data provide valuable information to businesses about customer demand and feedback. This information helps them determine the best locations to target for selling products, opening new stores, or advertising.
Improved Supply Chain Efficiency
The location data source can also enhance the existing FMCG supply chain by directing product delivery to its respective destinations. This reduces transportation expenses, eliminates wait time, and avoids poor stock conditions such as stockouts or excess stock.
Targeted Marketing and Sales Strategies
Marketing data can be primarily geographically oriented, so companies can choose the necessary areas and know local tastes and preferences. This advertising approach is an ideal approach as compared to the general campaign because it attracts more purchases and better customer response.
Better Customer Experience
Utilizing location data can improve the shopping experience and offer better promotions based on specific locations and customer preferences. This increases the chances of a purchase, boosts customer satisfaction, and eventually increases sales.
Competitive Advantage
Organizations that use location data effectively can be positioned more advantageously than their competitors because they can spot market niches overlooked by others. This assist them in dominating store sites and fulfilling customer demand efficiently.
Support for Sustainability Initiatives
Businesses use location data to ensure timely and efficient deliveries and cut costs through resource efficiency. This drives sustainable efforts and helps the company appeal to more environmentally conscious consumers.
Conclusion
Stakeholders need location analytics to describe how consumers exist and behave in their environment. This information informs marketers of the messages they intend to pass to their audience. Implementing location intelligence by outsourcing to LocationsCloud, an expert company, is critical in the FMCG business, given that consumer location information is the basis for making optimal decisions, increasing production, and improving customer experiences. The location data can be used to manage supply chains to their optimum, target marketing messages to geographies, select ideal locations for new stores, and generally perform all these actions in a way that has lower costs and is more sustainable.


